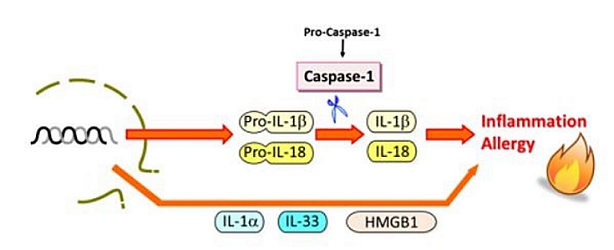
IL-18, is known as the IFN gamma-inducing factor, and as a proinflammatory cytokine, a member of the IL-1 family. Initially it is produced as an inactive pro-form and then secreted following maturation by caspase-1. IL-18 binds to the IL-18 receptor α (IL-18Rα) expressed on the surface of various cells (Kupffer cells, activated macrophages, keratinocytes, intestinal epithelial cells, osteoblasts, adrenal cortex cells and murine diencephalon) leading to inflammation. IL-18 also acts on T helper type-1 (Th1) T cells and in combination with IL-12 strongly induces them to produce IFN-γ. IL-18 has pleiotropic effects from enhancement production of IFN-γ and GM-CSF in peripheral blood mononuclear cells to production of Th1 cytokines, IL-2, GM-CSF and IFN-γ in T cells as well as the enhancement of Fas ligand expression by Th1 cells. Consequently, researchers are exploiting these regulatory processes for anti-tumor immune responses as IL-18 enhances antitumor immunity in various cancer types. The powerful activity of IL-18 in tumor models has emphasized the great attraction of IL-18 pathway as a target for tumor immunotherapy.
-
Research area
- Biochemicals
- Blood and Biospecimens
- Cell biology
- Environmental
- Flow Cytometry
- Forensic Science
- Genomics
- Immunology
- Labware
- Microbiology
- Pathology
- Transplantation
429 Too Many Requests 429 Too Many Requests
nginx - Products
- Suppliers
- About us
- Resources
- Events
- Support
- Lab Services
- Promotions