-
Research area
- Biochemicals
- Blood and Biospecimens
- Cell biology
- Environmental
- Flow Cytometry
- Forensic Science
- Genomics
- Immunology
- Labware
- Microbiology
- Pathology
- Transplantation
429 Too Many Requests 429 Too Many Requests
nginx - Products
- Suppliers
- About us
- Resources
- Events
- Support
- Lab Services
- Promotions
Product description
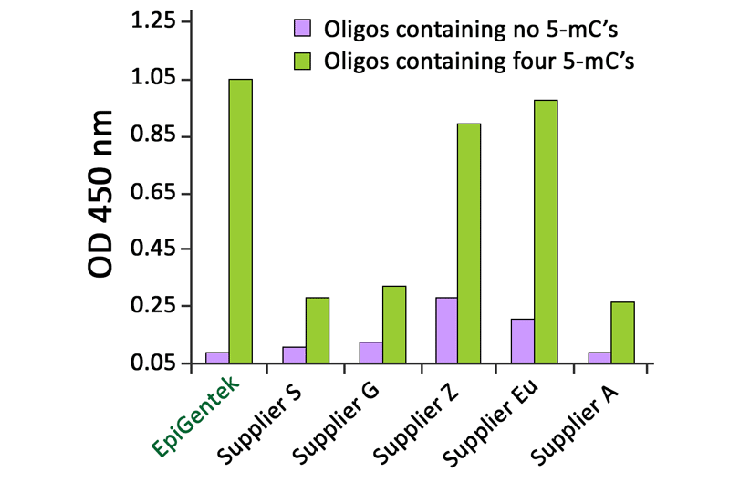
5-methylcytosine (5-mC) is formed when DNA methyltransferase (DNMT) catalyzes the addition of a methyl group onto the 5-carbon of the cytosine ring, an epigenetic process known as DNA methylation. 5-mC is considered the "fifth" DNA base and this 5-methylcytosine mouse monoclonal antibody is ideal for discriminating between the unmodified cytosine base (C) and the methylated cytosine base (5-mC) for DNA methylation studies. DNA methylation, the major epigenetic modification of eukaryotic genomes, plays an essential role in mammalian development. DNA methylation of promoter regions leads to inactivation of gene function. Also, DNA methylation status varies according to tissue type, and region-specific DNA hypermethylation and global DNA hypomethylation have been demonstrated to play an important role in tumorigenesis.
Specifications
Applications
IP, IHC, ELISA, IF, DB
Host
Mouse
Clonality
Monoclonal
Clone
33D3
Isotype
IgG1
Supplier
Epigentek
Shipping & storage
Shipping condition
Blue Ice
Storage temperature
-20°C
Do you have any questions about this product?
Order your product by email
Productname
5-Methylcytosine (5-mC) Monoclonal Antibody [33D3]
A-1014-010
By filling out this form, you are placing an order by e-mail. You will receive an order confirmation within one working day. The order cannot be modified after receipt of the order confirmation.
Request a sample
Productname
5-Methylcytosine (5-mC) Monoclonal Antibody [33D3]
A-1014-010
By filling out this form, you request a sample. You will receive an order confirmation within one working day. The order cannot be modified after receipt of the order confirmation.
Are you looking for specific products, alternatives or documentation?