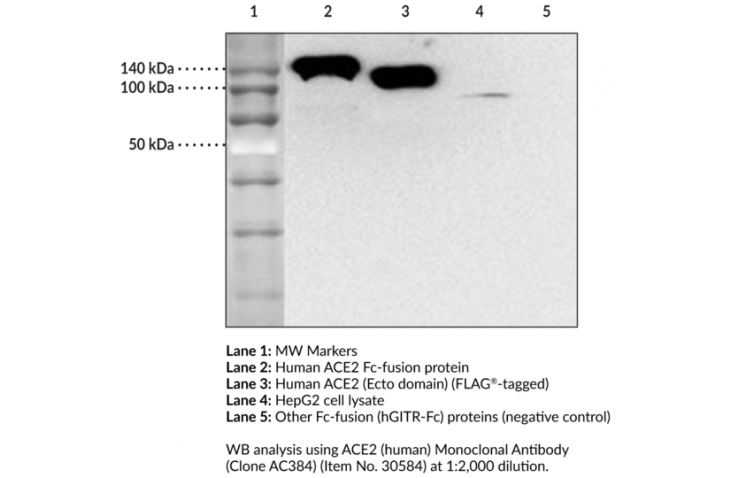
-
Research area
- Biochemicals
- Blood and Biospecimens
- Cell biology
- Environmental
- Flow Cytometry
- Forensic Science
- Genomics
- Immunology
- Labware
- Microbiology
- Pathology
- Transplantation
429 Too Many Requests 429 Too Many Requests
nginx - Suppliers
- About us
- Resources
- Events
- Support
- Lab Services
- Promotions
Product description
Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) is a carboxypeptidase and homolog of ACE1 that is encoded by ACE2 in humans.{53456,53457} It is a type I transmembrane protein composed of a cytoplasmic tail and an extracellular domain containing an HEMGH motif, characteristic of zinc-metallopeptidases, which exhibits carboxymonopeptidase activity.{53456} ACE2 is expressed in vascular endothelial cells where it catalyzes the conversion of angiotensin II to the vasodilatory peptide angiotensin 1-7 to regulate systemic blood pressure and angiotensin I to angiotensin 1-9, a peptide that counter-regulates the function of angiotensin II.{53456,53457,55475} It is also expressed in the epithelial cells of the kidney, heart, lung, small intestine, and liver and has roles in fluid homeostasis, cardiac contractility, and amino acid absorption, as well as the prevention of pulmonary fibrosis and hypertension. ACE2 also acts as a functional receptor for severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV) and SARS-CoV-2 to facilitate viral entry into host cells.{49542,53458} Cayman's ACE2 (human) Monoclonal Antibody (Clone AC384) can be used for ELISA and Western blot (WB) applications.
Specifications
Applications
WB, ELISA
Host
Mouse
Clone
AC384
Isotype
IgG1?
Supplier
Cayman Chemical
Shipping & storage
Shipping condition
Dry Ice
Storage temperature
-20°C
Do you have any questions about this product?
Order your product by email
Productname
ACE2 (human) Monoclonal Antibody (Clone AC384)
30584-50
By filling out this form, you are placing an order by e-mail. You will receive an order confirmation within one working day. The order cannot be modified after receipt of the order confirmation.
Request a sample
Productname
ACE2 (human) Monoclonal Antibody (Clone AC384)
30584-50
By filling out this form, you request a sample. You will receive an order confirmation within one working day. The order cannot be modified after receipt of the order confirmation.
Are you looking for specific products, alternatives or documentation?