-
Research area
- Biochemicals
- Blood and Biospecimens
- Cell biology
- Environmental
- Flow Cytometry
- Forensic Science
- Genomics
- Immunology
- Labware
- Microbiology
- Pathology
- Transplantation
429 Too Many Requests 429 Too Many Requests
nginx - Products
- Suppliers
- About us
- Resources
- Events
- Support
- Lab Services
- Promotions
Product description
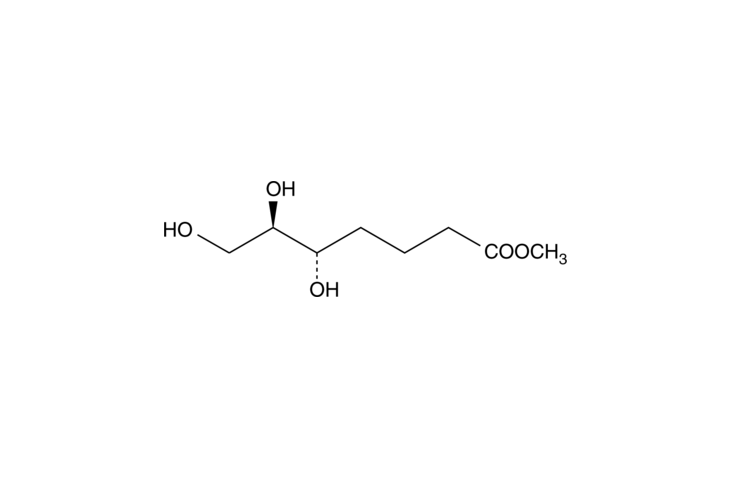
Lipoxins are trihydroxytetraene metabolites derived from arachidonic acid through an interaction between lipoxygenases with C-5 and C-15 specificities. Lipoxin A4 (LXA4) inhibits the chemotactic responsiveness of polymorphonuclear (PMN) neutrophils to leukotriene B4 and to the peptide formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine (fMLP).{14813} 5(S),6(R)-7-trihydroxymethyl Heptanoate is a C-7 truncated analog of lipoxin A4 (LXA4) that is equiactive as LXA4 in the inhibition of leukotriene B4 (LTB4)-induced polymorphonuclear neutrophils (PMN) chemotaxis with an IC50 value of 5nM.{14813}
Specifications
CAS number
78606-80-1
Supplier
Cayman Chemical
Shipping & storage
Shipping condition
Dry Ice
Storage temperature
-20°C
Do you have any questions about this product?
Order your product by email
Productname
5(S),6(R)-7-trihydroxymethyl Heptanoate
10005032-1
By filling out this form, you are placing an order by e-mail. You will receive an order confirmation within one working day. The order cannot be modified after receipt of the order confirmation.
Request a sample
Productname
5(S),6(R)-7-trihydroxymethyl Heptanoate
10005032-1
By filling out this form, you request a sample. You will receive an order confirmation within one working day. The order cannot be modified after receipt of the order confirmation.
Are you looking for specific products, alternatives or documentation?